Cold storage technologies
Reasons and benefits of using a cold storage
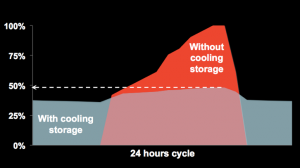
» To reduce chillers capacity
» To reduce electricity demand charge
» To optimize energy consumptions of buildings air conditioning
» To dispose of a spare cooling capacity in case of a breakdown or power failure
Different types of cold storages
Either water or ice are used to store cold energy. However while cold water can store 10 kWh per m3 of storage tank, ice is more efficient and can store 50 kWh per m3 of storage tank.
Ice storages include two broad categories
Ice on coils which consist of producing ice around pipes immerged into water
Encapsulated ice where ice is formed in basic plastic capsules
Ice Ball and Ice Spray technologies developed by Cryogel are encapsulated ice systems
Cold storage technologies comparison
CRYOGEL technologies
Other technologies
Ice Spray
Atmospheric tankHeat exchange
Brine sprayed on the spheres from the top of the tank
Stored energy :
50 kWh per m3
Tank storage characteristics :
Any size, shape or material
Insulated and water proofed on site.
Piling up to 10 meters.
Ice Ball
Pressurized tankHeat exchange
Brine circulation inside the tank and around the immerged spheres
Stored energy :
50 kWh per m3
Recommended tank storage characteristics :
Horizontal layout
Maximum tank size 100 m3, equivalent to 5000 kWh,
Maximum tank diameter : 3m
Ice on coils (internal)
Atmospheric tankHeat exchange
Brine circulation inside immerged tubes in water to be frozen
Stored energy :
50 kWh per m3
Tank storage characteristics :
Usually smaller than 5000 kWh per unit
Limited storage height.
Chilled water
Atmospheric tankHeat exchange
No glycol used, the exchange is direct
Stored energy :
10 kWh per m3
Tank storage characteristics :
Limited by ground surface and weight
Must be round to support efforts, minimum height required for the stratification.